Bloom Taxonomy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Bloom Taxonomy = | = Bloom Taxonomy = | ||
[[File:Bloom.png|thumb]] | |||
== Remembering (Knowledge / Recall) == | == Remembering (Knowledge / Recall) == | ||
🧠 At this level, an expert can **define** Bloom’s taxonomy and **name** its | 🧠 At this level, an expert can **define** Bloom’s taxonomy and **name** its foundational terms, contributors, versions, and common usage contexts. | ||
* '''Core terminology & definitions''' | * '''Core terminology & definitions''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_taxonomy Bloom's taxonomy]''' – A hierarchical framework for classifying educational learning objectives in the '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_domain cognitive domain]''', progressing from simple recall to complex creation. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_domain Cognitive domain]''' – The area of learning related to mental skills, knowledge acquisition, and reasoning. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affective_domain Affective domain]''' – The learning domain involving attitudes, emotions, values, and feelings. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychomotor_learning Psychomotor domain]''' – The learning domain focused on physical movement, coordination, and motor skills. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_objective Learning objective]''' – A measurable statement describing what a learner should know or do after instruction. | ||
** [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxonomy_of_educational_objectives | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_outcome Learning outcome]''' – The demonstrated result or performance showing that learning has occurred. | ||
** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taxonomy_of_educational_objectives Taxonomy of Educational Objectives]''' – The original publication series introducing Bloom’s taxonomy. | |||
* '''Key contributors''' | * '''Key contributors''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benjamin_Bloom Benjamin Bloom]''' – Educational psychologist who led the committee that developed the taxonomy. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/David_Krathwohl David Krathwohl]''' – Co-author of the taxonomy and contributor to the revised version. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorin_W._Anderson Lorin Anderson]''' – Former student of Bloom who co-led the 2001 revision. | ||
* '''Canonical versions''' | * '''Canonical versions''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_taxonomy#Original_taxonomy Original 1956 taxonomy]''' – Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_taxonomy#Revised_taxonomy Revised 2001 taxonomy]''' – Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, Create. | ||
* '''Where Bloom’s taxonomy commonly | * '''Where Bloom’s taxonomy is commonly seen''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education Education]''' – Curriculum development, lesson planning, learning progressions. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instructional_design Instructional design]''' – Structuring learning activities and assessments. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Educational_assessment Educational assessment]''' – Categorizing question difficulty and cognitive demand. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teacher_education Teacher education]''' – Training educators in objective-writing and pedagogy. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corporate_training Corporate training]''' – Designing workplace learning pathways and upskilling programs. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_management_system Learning management systems]''' – Tagging objectives and item banks by Bloom level. | ||
* '''Typical recall-level facts''' | * '''Typical recall-level facts''' | ||
** | ** Bloom’s taxonomy contains **six cognitive levels** in its revised form. | ||
** It originated in the United States in the 1950s. | ** It originated in the **United States** in the **1950s**. | ||
** It is widely used | ** It is one of the **most widely used educational frameworks** worldwide. | ||
** It appears in textbooks, standards documents, teacher preparation programs, and training manuals. | |||
== Understanding (Comprehension) == | == Understanding (Comprehension) == | ||
📖 | 📖 At this level, an expert can **explain**, **summarize**, and **compare** concepts related to Bloom’s taxonomy and describe how its pieces fit together. | ||
* Conceptual relationships & contrasts | * '''Conceptual relationships & contrasts''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_taxonomy#Original_taxonomy Original Bloom’s taxonomy]''' vs. '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_taxonomy#Revised_taxonomy Revised taxonomy]''' – The former uses noun-based level names; the latter uses action verbs and places "Create" above "Evaluate." | ||
** [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_domain Cognitive domain]''' vs. '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affective_domain Affective domain]''' vs. '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychomotor_learning Psychomotor domain]''' – Three complementary learning domains, not competing models. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOLO_taxonomy SOLO taxonomy]''' – An alternative framework focused on structural complexity rather than cognitive processes. | ||
* Core principles & paradigms | * '''Core principles & paradigms''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hierarchy Hierarchical learning progression]''' – Complex reasoning builds upon foundational knowledge. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Constructivism_(philosophy_of_education) Constructivist learning theory]''' – Learners actively construct meaning rather than absorb facts. | ||
** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scaffolding Novice-to-expert scaffolding]''' – Instruction should guide learners upward through cognitive levels. | |||
* Core operational concepts | * '''Core operational concepts — how Bloom’s taxonomy works''' | ||
** | ** Levels signal the **expected cognitive demand**, not task difficulty or time required. | ||
** | ** Action verbs help classify tasks, but must be interpreted within context. | ||
** Assessments, instruction, and objectives should remain **aligned** across levels. | |||
* Producer vs. consumer perspectives | * '''Producer vs. consumer perspectives''' | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instructional_design Instructional designer]''' – Uses Bloom to craft measurable, level-appropriate objectives. | ||
** | ** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teacher Teacher]''' – Selects activities and assessments targeting specific Bloom levels. | ||
** '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student Student]''' – Demonstrates mastery through performance aligned with the intended cognitive level. | |||
* '''Typical comprehension-level abilities''' | |||
** Can restate the purpose of Bloom’s taxonomy. | |||
** Can explain why multiple levels exist. | |||
** Can distinguish remembering from understanding, and understanding from applying. | |||
** Can summarize the impact of Bloom’s taxonomy on modern education. | |||
== Applying (Use / Application) == | |||
** | 🛠️ At this level, an expert can **use** Bloom’s taxonomy in real instructional, assessment, or design situations. | ||
** | |||
* | * '''"Hello, World" examples''' | ||
** | ** Writing measurable learning objectives using Bloom-level verbs. | ||
** | ** Rewriting existing test questions to intentionally target a higher/lower cognitive level. | ||
* | * '''Guides for core task loops''' | ||
** | ** Using the taxonomy within '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backward_design backward design]''' — define outcomes → plan assessments → plan instruction. | ||
** | ** Applying Bloom levels during '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curriculum curriculum]''' alignment and course sequencing. | ||
** Categorizing exam items with '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Educational_assessment educational assessment]''' frameworks. | |||
* | * '''Reference of common actions / “cheatsheet”''' | ||
** | ** Remember → list, define, label | ||
** | ** Understand → summarize, interpret, classify | ||
** Apply → execute, demonstrate, implement | |||
** Analyze → compare, differentiate, attribute | |||
** Evaluate → judge, justify, critique | |||
** Create → design, produce, generate | |||
* '''Contextual use cases''' | |||
** Mapping training activities in '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corporate_training corporate learning programs]'''. | |||
** Designing question banks in a '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_management_system learning management system]'''. | |||
** Ensuring alignment in multi-instructor courses or programs. | |||
* | * '''Typical application-level abilities''' | ||
** | ** Can classify instructional materials by Bloom level. | ||
** | ** Can select appropriate teaching strategies for each level. | ||
** Can revise objectives to improve clarity and measurability. | |||
---- | |||
* Troubleshooting & observability techniques | == Analyzing (Break Down / Analysis) == | ||
** | 🔬 At this level, an expert can **examine structure**, **identify patterns**, and **compare** Bloom’s taxonomy with alternatives. | ||
** | |||
* '''Comparative analysis''' | |||
** Bloom’s taxonomy vs. '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOLO_taxonomy SOLO taxonomy]''' — cognitive processes vs. structural complexity. | |||
** Bloom’s taxonomy vs. '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andragogy andragogy]''' — task complexity vs. adult-learning orientation. | |||
* '''Failure modes & root causes''' | |||
** Treating Bloom levels as a ranking of **worthiness**, not cognitive demand. | |||
** Over-reliance on verb lists without examining assignment context. | |||
** Assuming every lesson must target the highest level. | |||
* '''Troubleshooting & observability techniques''' | |||
** Conducting a '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curriculum_mapping curriculum map]''' to detect level imbalance (too much recall, not enough analysis). | |||
** Reviewing assessment validity through '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_analytics learning analytics]''' and performance patterns. | |||
** Spot-checking rubrics for alignment drift. | |||
* '''Structural insights''' | |||
** Bloom’s taxonomy organizes cognitive skills **hierarchically**, not categorically. | |||
** Levels support **progression**, not segmentation — learners move fluidly. | |||
* '''Typical analysis-level abilities''' | |||
** Can critique a lesson plan using Bloom’s taxonomy. | |||
** Can identify mismatched objectives, activities, and assessments. | |||
** Can explain why a task belongs to a specific level. | |||
---- | |||
== Creating (Synthesis / Create) == | == Creating (Synthesis / Create) == | ||
🏗️ | 🏗️ At this level, an expert can **design**, **invent**, and **integrate** Bloom’s taxonomy into new instructional systems or models. | ||
* '''Design patterns & best practices''' | |||
** Using Bloom levels to scaffold increasingly complex learning experiences. | |||
** Embedding Bloom-aligned formative assessments into teaching cycles. | |||
* '''Ethical & equity considerations''' | |||
** Ensuring all learners—not only advanced ones—access higher-order thinking. | |||
** Avoiding structural bias in expectations or learning pathways. | |||
* '''Lifecycle management strategies''' | |||
** Periodically revising program objectives to reflect evolving competencies. | |||
** Maintaining consistency across departments, schools, or institutions. | |||
* '''Scalability & optimization patterns''' | |||
** Integrating taxonomy tagging into question banks in a '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Learning_management_system learning management system]'''. | |||
** Using Bloom-based metadata for adaptive-learning personalization. | |||
* | * '''Typical creation-level abilities''' | ||
** | ** Can build new curricula around progressive cognitive development. | ||
** | ** Can design assessments intentionally targeting higher levels. | ||
** Can create institution-wide Bloom usage guidelines. | |||
---- | |||
* | == Evaluating (Judgment / Evaluation) == | ||
** | ⚖️ At this level, an expert can **judge effectiveness**, **assess quality**, and **make strategic decisions** about Bloom’s taxonomy in practice. | ||
** | |||
* | * '''Evaluation frameworks & tools''' | ||
** [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | ** Measuring alignment through '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Program_evaluation program evaluation]'''. | ||
** | ** Reviewing assessment rigor using '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Educational_measurement educational measurement]''' methods. | ||
** Determining instructional impact via '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Student_engagement student engagement]''' indicators. | |||
* '''Maturity & adoption models''' | |||
** Analyzing institutional uptake using '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffusion_of_innovations diffusion of innovations]''' theory. | |||
** Considering organizational readiness, training, and support resources. | |||
* | * '''Key performance indicators''' | ||
** | ** Distribution of learning outcomes across Bloom levels. | ||
** | ** Assessment validity, knowledge transfer, retention, and performance. | ||
* | * '''Strategic decision criteria''' | ||
** | ** Whether Bloom’s taxonomy or '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOLO_taxonomy SOLO taxonomy]''' better fits specific instructional goals. | ||
** | ** Cost–benefit trade-offs for training, implementation, and maintenance. | ||
* | * '''Holistic impact analysis''' | ||
** | ** Workload, clarity, pedagogical benefit, faculty adoption, student experience. | ||
** Alignment with broader '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pedagogy pedagogy]''' and '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education_policy education policy]''' frameworks. | |||
* | * '''Typical evaluation-level abilities''' | ||
** | ** Can judge whether Bloom’s taxonomy is being applied appropriately. | ||
** | ** Can recommend improvements based on evidence and outcomes. | ||
** Can determine whether Bloom is the right framework for the context. | |||
[[Category:Education]] | [[Category:Education]] | ||
[[Category:Instructional Design]] | [[Category:Instructional Design]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:34, 24 November 2025
Bloom Taxonomy[edit]
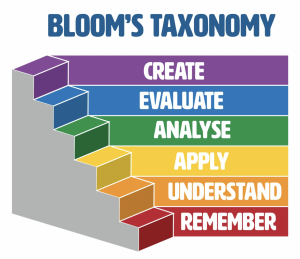
Remembering (Knowledge / Recall)[edit]
🧠 At this level, an expert can **define** Bloom’s taxonomy and **name** its foundational terms, contributors, versions, and common usage contexts.
- Core terminology & definitions
- Bloom's taxonomy – A hierarchical framework for classifying educational learning objectives in the cognitive domain, progressing from simple recall to complex creation.
- Cognitive domain – The area of learning related to mental skills, knowledge acquisition, and reasoning.
- Affective domain – The learning domain involving attitudes, emotions, values, and feelings.
- Psychomotor domain – The learning domain focused on physical movement, coordination, and motor skills.
- Learning objective – A measurable statement describing what a learner should know or do after instruction.
- Learning outcome – The demonstrated result or performance showing that learning has occurred.
- Taxonomy of Educational Objectives – The original publication series introducing Bloom’s taxonomy.
- Key contributors
- Benjamin Bloom – Educational psychologist who led the committee that developed the taxonomy.
- David Krathwohl – Co-author of the taxonomy and contributor to the revised version.
- Lorin Anderson – Former student of Bloom who co-led the 2001 revision.
- Canonical versions
- Original 1956 taxonomy – Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation.
- Revised 2001 taxonomy – Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, Create.
- Where Bloom’s taxonomy is commonly seen
- Education – Curriculum development, lesson planning, learning progressions.
- Instructional design – Structuring learning activities and assessments.
- Educational assessment – Categorizing question difficulty and cognitive demand.
- Teacher education – Training educators in objective-writing and pedagogy.
- Corporate training – Designing workplace learning pathways and upskilling programs.
- Learning management systems – Tagging objectives and item banks by Bloom level.
- Typical recall-level facts
- Bloom’s taxonomy contains **six cognitive levels** in its revised form.
- It originated in the **United States** in the **1950s**.
- It is one of the **most widely used educational frameworks** worldwide.
- It appears in textbooks, standards documents, teacher preparation programs, and training manuals.
Understanding (Comprehension)[edit]
📖 At this level, an expert can **explain**, **summarize**, and **compare** concepts related to Bloom’s taxonomy and describe how its pieces fit together.
- Conceptual relationships & contrasts
- Original Bloom’s taxonomy vs. Revised taxonomy – The former uses noun-based level names; the latter uses action verbs and places "Create" above "Evaluate."
- Cognitive domain vs. Affective domain vs. Psychomotor domain – Three complementary learning domains, not competing models.
- SOLO taxonomy – An alternative framework focused on structural complexity rather than cognitive processes.
- Core principles & paradigms
- Hierarchical learning progression – Complex reasoning builds upon foundational knowledge.
- Constructivist learning theory – Learners actively construct meaning rather than absorb facts.
- Novice-to-expert scaffolding – Instruction should guide learners upward through cognitive levels.
- Core operational concepts — how Bloom’s taxonomy works
- Levels signal the **expected cognitive demand**, not task difficulty or time required.
- Action verbs help classify tasks, but must be interpreted within context.
- Assessments, instruction, and objectives should remain **aligned** across levels.
- Producer vs. consumer perspectives
- Instructional designer – Uses Bloom to craft measurable, level-appropriate objectives.
- Teacher – Selects activities and assessments targeting specific Bloom levels.
- Student – Demonstrates mastery through performance aligned with the intended cognitive level.
- Typical comprehension-level abilities
- Can restate the purpose of Bloom’s taxonomy.
- Can explain why multiple levels exist.
- Can distinguish remembering from understanding, and understanding from applying.
- Can summarize the impact of Bloom’s taxonomy on modern education.
Applying (Use / Application)[edit]
🛠️ At this level, an expert can **use** Bloom’s taxonomy in real instructional, assessment, or design situations.
- "Hello, World" examples
- Writing measurable learning objectives using Bloom-level verbs.
- Rewriting existing test questions to intentionally target a higher/lower cognitive level.
- Guides for core task loops
- Using the taxonomy within backward design — define outcomes → plan assessments → plan instruction.
- Applying Bloom levels during curriculum alignment and course sequencing.
- Categorizing exam items with educational assessment frameworks.
- Reference of common actions / “cheatsheet”
- Remember → list, define, label
- Understand → summarize, interpret, classify
- Apply → execute, demonstrate, implement
- Analyze → compare, differentiate, attribute
- Evaluate → judge, justify, critique
- Create → design, produce, generate
- Contextual use cases
- Mapping training activities in corporate learning programs.
- Designing question banks in a learning management system.
- Ensuring alignment in multi-instructor courses or programs.
- Typical application-level abilities
- Can classify instructional materials by Bloom level.
- Can select appropriate teaching strategies for each level.
- Can revise objectives to improve clarity and measurability.
Analyzing (Break Down / Analysis)[edit]
🔬 At this level, an expert can **examine structure**, **identify patterns**, and **compare** Bloom’s taxonomy with alternatives.
- Comparative analysis
- Bloom’s taxonomy vs. SOLO taxonomy — cognitive processes vs. structural complexity.
- Bloom’s taxonomy vs. andragogy — task complexity vs. adult-learning orientation.
- Failure modes & root causes
- Treating Bloom levels as a ranking of **worthiness**, not cognitive demand.
- Over-reliance on verb lists without examining assignment context.
- Assuming every lesson must target the highest level.
- Troubleshooting & observability techniques
- Conducting a curriculum map to detect level imbalance (too much recall, not enough analysis).
- Reviewing assessment validity through learning analytics and performance patterns.
- Spot-checking rubrics for alignment drift.
- Structural insights
- Bloom’s taxonomy organizes cognitive skills **hierarchically**, not categorically.
- Levels support **progression**, not segmentation — learners move fluidly.
- Typical analysis-level abilities
- Can critique a lesson plan using Bloom’s taxonomy.
- Can identify mismatched objectives, activities, and assessments.
- Can explain why a task belongs to a specific level.
Creating (Synthesis / Create)[edit]
🏗️ At this level, an expert can **design**, **invent**, and **integrate** Bloom’s taxonomy into new instructional systems or models.
- Design patterns & best practices
- Using Bloom levels to scaffold increasingly complex learning experiences.
- Embedding Bloom-aligned formative assessments into teaching cycles.
- Ethical & equity considerations
- Ensuring all learners—not only advanced ones—access higher-order thinking.
- Avoiding structural bias in expectations or learning pathways.
- Lifecycle management strategies
- Periodically revising program objectives to reflect evolving competencies.
- Maintaining consistency across departments, schools, or institutions.
- Scalability & optimization patterns
- Integrating taxonomy tagging into question banks in a learning management system.
- Using Bloom-based metadata for adaptive-learning personalization.
- Typical creation-level abilities
- Can build new curricula around progressive cognitive development.
- Can design assessments intentionally targeting higher levels.
- Can create institution-wide Bloom usage guidelines.
Evaluating (Judgment / Evaluation)[edit]
⚖️ At this level, an expert can **judge effectiveness**, **assess quality**, and **make strategic decisions** about Bloom’s taxonomy in practice.
- Evaluation frameworks & tools
- Measuring alignment through program evaluation.
- Reviewing assessment rigor using educational measurement methods.
- Determining instructional impact via student engagement indicators.
- Maturity & adoption models
- Analyzing institutional uptake using diffusion of innovations theory.
- Considering organizational readiness, training, and support resources.
- Key performance indicators
- Distribution of learning outcomes across Bloom levels.
- Assessment validity, knowledge transfer, retention, and performance.
- Strategic decision criteria
- Whether Bloom’s taxonomy or SOLO taxonomy better fits specific instructional goals.
- Cost–benefit trade-offs for training, implementation, and maintenance.
- Holistic impact analysis
- Workload, clarity, pedagogical benefit, faculty adoption, student experience.
- Alignment with broader pedagogy and education policy frameworks.
- Typical evaluation-level abilities
- Can judge whether Bloom’s taxonomy is being applied appropriately.
- Can recommend improvements based on evidence and outcomes.
- Can determine whether Bloom is the right framework for the context.